Canadian Occupational Projection System (COPS)
Industrial Summary
Wholesale Trade
(NAICS 4111-4191)
This industry comprises establishments primarily engaged in wholesaling merchandise, and providing related logistic, marketing and support services. The wholesaling process is generally an intermediate step in the distribution of merchandise in large quantities to retailers, businesses and institutions. Machinery, equipment and supplies is the most important segment within the industry, accounting for 28% of production and 30% of employment in 2023. Other key segments include personal and household goods (17% of production and 12% of employment), building material and supplies (13%, 18%), food and beverages (13%, 15%), and motor vehicles and parts (9%, 6%). The industry employed 690,100 workers in 2023, mostly concentrated in Ontario (41%), Quebec (21%), Alberta (14%) and British Columbia (13%), with a workforce mainly composed of men (69%).
Key occupations (5-digit NOC) include:
- Sales and account representatives - wholesale trade (non-technical) (64101)
- Technical sales specialists - wholesale trade (62100)
- Retail and wholesale trade managers (60020)
- Material handlers (75101)
- Transport truck divers (73300)
- Shippers and receivers (14400)
- Supervisors, supply chain, tracking and scheduling co-ordination occupations (12013)
- Heavy-duty equipment mechanics (72401)
- Retail and wholesale buyers (62101)
- Accounting and related clerks (14200)
- Production and transportation logistics coordinators (13201)
- Purchasing and inventory control workers (14403)
Projections over the 2024-2033 period
Real GDP is projected to grow at an average annual rate of 1.6%. Current low levels of inventories suggest that businesses will seek to restock to meet growing demand from consumers and businesses. The industry, which distributes merchandise to various businesses in addition to retailers, is expected to benefit from robust growth in business investment related to machinery and equipment and engineering structures and growth in housing and the construction of non-residential buildings. On the consumer side, while consumption is expected to be robust in the short-term as interest rates go down, high mortgage debt and an aging population will limit spending in the long term.
Productivity is expected to grow at an average annual rate of 1.1%. Productivity in the wholesale trade sector is expected to significantly improve, thanks to the growing adoption of new technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), advanced data analytics, cloud infrastructure, collaboration tools and security software tools. These technologies will enable wholesalers to optimize their operations, reduce waste, and respond more quickly to market demand.
Employment is projected to increase by 0.5% annually. With strong expected growth in productivity, employment gains are projected to be somewhat limited. The adoption of productivity-enhancing technologies related to inventory management and other logistical services are expected to continue to restrain job creation in the industry (especially for jobs involving repetitive tasks), while sensor-enhanced robotics might threaten on-the-floor jobs (such as fork-lift drivers).
Challenges and Opportunities
The primary challenge facing the industry is the need to adopt advanced technologies. While some wholesalers may delay this transition—since ongoing operations do not always demand immediate investment—high implementation costs can also be a deterrent. To address these barriers, many wholesalers identified government grants and contribution programs as the most valuable forms of support for technology-related investments. Over time, those who fail to modernize risk falling behind their competitors, both within the country and on the global stage. Increased competition from e-commerce, on-demand production and other direct-to-customer operations by manufacturers that bypass intermediates will also have many implications for supply chains and for storage, pressuring wholesalers to restructure their operations by lowering labour costs and adopting automation enhancing machinery.
Real GDP , Employment and Productivity Growth rate (2024-2033)
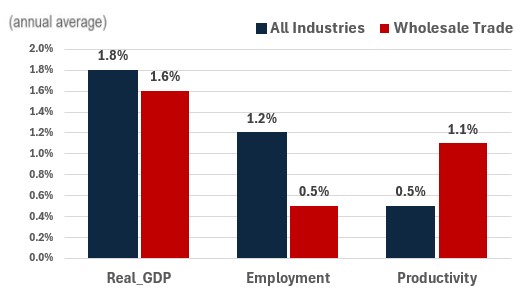
Sources: ESDC 2024 COPS projections.
| Real GDP | Employment | Productivity | |
|---|---|---|---|
| All Industries | 1.8 | 1.2 | 0.5 |
| Wholesale Trade | 1.6 | 0.5 | 1.1 |